Tiny House Plans With Cost To Build: A Comprehensive Guide
The tiny house movement has gained significant traction in recent years, driven by a desire for simplified living, financial freedom, and environmental responsibility. Building a tiny house, however, requires careful planning and consideration, particularly when it comes to selecting the right plans and understanding the associated costs. This article provides a comprehensive overview of tiny house plans and the factors influencing the cost to build, offering valuable insights for individuals considering embarking on this unique building project.
Understanding Tiny House Plans: Types and Considerations
Tiny house plans encompass a wide range of designs, each tailored to different lifestyles, needs, and aesthetic preferences. Choosing the right plan is paramount to ensuring a functional, comfortable, and structurally sound tiny home. Plans can be categorized based on several factors, including size, foundation type, style, and complexity.
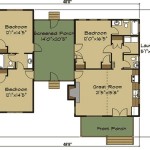
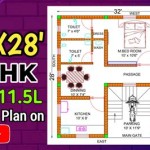
Size: Tiny houses are generally defined as dwellings under 400 square feet. Plans are available for various sizes within this range, from extremely compact models under 200 square feet to larger options approaching the upper limit. The ideal size depends on the number of occupants, lifestyle requirements, and intended use of the space. A single person might thrive in a smaller dwelling, while a couple or small family may require a larger footprint to maintain comfortable living.
Foundation Type: Tiny houses can be built on a foundation or on wheels. Foundation-based tiny houses are typically more permanent structures, subject to local building codes and regulations. These houses require a traditional foundation, such as a concrete slab, pier, or crawl space. On the other hand, tiny houses on wheels (THOWs) offer greater mobility and flexibility. These houses are built on a trailer and can be moved relatively easily. However, THOWs may be subject to regulations governing recreational vehicles (RVs) or park model homes, depending on the jurisdiction.
Style: Tiny house plans are available in a variety of architectural styles, ranging from minimalist modern to rustic farmhouse. The choice of style is largely a matter of personal preference, but it's important to consider the overall aesthetic and how it integrates with the surrounding environment. Common styles include contemporary, traditional, Scandinavian, and bohemian.
Complexity: The complexity of a tiny house plan can significantly impact the cost and time required for construction. Simple, rectangular designs are generally easier and less expensive to build than more intricate designs with multiple angles, curves, or custom features. Complexity also extends to the internal layout and systems, such as plumbing, electrical, and HVAC. Off-grid systems, for example, can add significant complexity and cost to the project.
When selecting a tiny house plan, it is essential to carefully consider the following factors:
- Budget: Establish a realistic budget for the entire project, including the cost of the plan, materials, labor, permits, and other expenses.
- Building Codes and Regulations: Research local building codes and regulations to ensure compliance. This is particularly important for foundation-based tiny houses, which are subject to stricter requirements than THOWs.
- Skill Level: Assess your own skills and experience in construction. If you are not comfortable with certain aspects of the project, consider hiring a professional contractor or subcontractor.
- Lifestyle and Needs: Choose a plan that meets your specific lifestyle and needs, considering factors such as space requirements, storage, and accessibility.
- Future Considerations: Think about your long-term plans for the tiny house. Will you be living in it permanently, or will it be used as a vacation home or rental property? This can influence your choice of plan and features.
Estimating the Cost to Build a Tiny House
Determining the cost to build a tiny house is a complex process, as it depends on a variety of factors, including the size and complexity of the plan, the materials used, the location of the project, and whether you hire professional labor or DIY the construction. A detailed breakdown of potential costs is essential for effective budgeting and financial planning.
Plan Costs: The cost of tiny house plans can vary widely, ranging from free online plans to professionally designed architectural drawings. Free plans may be suitable for simple designs, but they may lack the detail and accuracy required for more complex projects. Professionally designed plans can provide greater assurance of structural integrity and code compliance, but they come at a higher cost.
Materials: Material costs account for a significant portion of the overall budget. The type of materials used can also significantly affect the price. Factors influencing material costs include:
- Lumber: The cost of lumber can fluctuate depending on market conditions and the type of wood used.
- Insulation: Insulation is critical for energy efficiency and comfort. Options include fiberglass, spray foam, and rigid foam.
- Roofing: Roofing materials vary in price and durability. Common options include asphalt shingles, metal roofing, and wood shakes.
- Siding: Siding materials also vary in price and durability. Options include wood siding, vinyl siding, and metal siding.
- Windows and Doors: Energy-efficient windows and doors can help reduce energy consumption and improve comfort.
- Plumbing and Electrical: The cost of plumbing and electrical materials depends on the complexity of the systems and the quality of the fixtures.
- Appliances: The cost of appliances depends on the size, features, and energy efficiency of the units.
- Interior Finishes: Interior finishes, such as flooring, cabinetry, and countertops, can significantly impact the overall cost.
Labor Costs: If you plan to hire professional contractors or subcontractors, labor costs can add a substantial expense. Labor costs vary depending on the location, the complexity of the project, and the experience of the workers. Tasks that typically require professional assistance include:
- Foundation work
- Framing
- Plumbing
- Electrical
- HVAC
- Roofing
Permits and Fees: Building permits and other fees are required for most tiny house projects, particularly those built on a foundation. Permit costs vary depending on the location and the type of project. Failure to obtain the necessary permits can result in fines and delays.
Other Expenses: In addition to the above costs, there are several other expenses to consider, including:
- Tools and Equipment: If you plan to DIY some or all of the construction, you will need to purchase or rent tools and equipment.
- Transportation: Transportation costs can include the cost of transporting materials to the building site.
- Insurance: Insurance is essential to protect against liability and property damage.
- Contingency Fund: It is always wise to set aside a contingency fund to cover unexpected expenses or delays. A common recommendation is 10-20% of the overall budget.
A rough estimate for building a tiny house can range from $30,000 to $80,000 or more, but this can vary significantly. DIY projects typically cost less than those involving professional labor. Choosing less expensive materials and simplifying the design can also help reduce costs. Thorough budgeting and careful planning are crucial to controlling costs and ensuring a successful project.
Key Strategies for Cost Optimization
While the cost of building a tiny house can seem daunting, there are several strategies that can be employed to optimize costs without compromising quality or functionality. These strategies involve careful planning, material selection, and labor management.
DIY Construction: Performing as much of the construction work as possible can significantly reduce labor costs. This requires a willingness to learn new skills and dedicate significant time and effort to the project. Tasks that are often suitable for DIY include framing, insulation, siding, and interior finishing. However, it is crucial to be realistic about your skills and limitations and to seek professional assistance when needed.
Material Sourcing: Sourcing materials strategically can lead to significant cost savings. Consider the following tips:
- Shop around: Compare prices from different suppliers to find the best deals.
- Buy in bulk: Purchasing materials in bulk can often result in discounts.
- Consider reclaimed materials: Reclaimed or recycled materials can be a cost-effective and environmentally friendly alternative to new materials.
- Look for sales and discounts: Keep an eye out for sales and discounts on building materials.
Design Simplification: Simplifying the design of the tiny house can significantly reduce both material and labor costs. This can involve choosing a simple rectangular shape, minimizing the number of windows and doors, and avoiding complex architectural details. A streamlined design is often more cost-effective to build and maintain.
Efficient Space Planning: Maximizing the use of space is crucial in a tiny house. Efficient space planning can reduce the need for additional square footage, thereby lowering overall costs. Consider incorporating multi-functional furniture, such as sofa beds and storage ottomans, to optimize space utilization.
Strategic Systems Design: Carefully consider the design of the plumbing, electrical, and HVAC systems to minimize costs. Simple, efficient systems are generally less expensive to install and maintain. Consider using energy-efficient appliances and fixtures to reduce long-term operating costs.
Phased Construction: Breaking the construction project into phases can help manage costs and allow for flexibility. This involves prioritizing essential tasks, such as building the shell of the house, and deferring less critical tasks, such as landscaping or installing decorative features, until later.
By implementing these cost optimization strategies, individuals can significantly reduce the cost of building a tiny house without sacrificing quality or functionality. Careful planning, strategic material sourcing, and efficient labor management are essential for achieving a successful and affordable tiny house project.

16 Cutest Tiny Home Plans With Cost To Build Craft Mart

16 Cutest Tiny Home Plans With Cost To Build Craft Mart

16 Cutest Tiny Home Plans With Cost To Build House Floor Round

10 X 20 Tiny Home Designs Floorplans Costs And Inspiration The Life

Floor Plans For Tiny Houses Besting A Frames Cabins Sheds House Small Unique

16 Cutest Tiny Home Plans With Cost To Build Craft Mart

Build Your Own Tiny House How To Minimize The Building Cost Top Ing Home Plans

13 Best Small Cabin Plans With Cost To Build Floor

16 Cutest Tiny Home Plans With Cost To Build Craft Mart
Est House Plans To Build Simple With Style Blog Eplans Com