Single Story Small Home Plans: Efficiency and Accessibility in Design
Single story small home plans represent a growing trend in residential architecture. Their appeal stems from a combination of factors, including affordability, accessibility, ease of maintenance, and adaptability to diverse lifestyles. These plans prioritize efficient use of space without sacrificing comfort or aesthetic appeal. The design considerations for such homes differ significantly from larger, multi-story dwellings, necessitating a careful approach to layout, material selection, and overall functionality.
The focus on single-level living simplifies daily routines, particularly for individuals with mobility limitations or those seeking age-in-place solutions. The elimination of stairs reduces the risk of falls and makes the home more accessible to wheelchair users or people with other physical challenges. Furthermore, single story designs often integrate universal design principles, promoting inclusivity and comfort for all occupants.
The cost-effectiveness of single story small homes is another significant advantage. Lower construction costs, reduced heating and cooling expenses, and simplified maintenance contribute to long-term financial savings. The smaller footprint requires less land, making these homes suitable for urban infill lots or downsizing scenarios. This article will explore the key considerations involved in planning a single story small home, covering aspects such as space optimization, design styles, and sustainability features.
Space Optimization and Layout Design
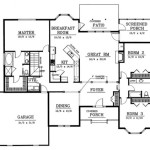
Maximizing usable space is paramount in single story small home plans. Every square foot must be carefully considered to ensure functionality and comfort. Open-concept layouts are frequently employed to create a sense of spaciousness and improve circulation. The combination of living, dining, and kitchen areas into a single, flowing space minimizes the need for interior walls, thereby expanding the perceived size of the home.
Storage solutions are critical in small homes. Built-in cabinetry, closet organizers, and multi-functional furniture can help to minimize clutter and maximize available space. Vertical storage, such as shelving that extends to the ceiling, is an effective way to utilize unused space. Under-bed storage, hidden compartments, and pull-out drawers can also provide valuable storage options without compromising the functionality of the living areas.
Strategic placement of windows and doors can significantly impact the perceived size and comfort of a small home. Large windows and sliding glass doors allow for ample natural light, which can make a space feel brighter and more spacious. Orientation of the home to maximize sunlight exposure can also reduce the need for artificial lighting and heating. Thoughtful consideration of window placement can also provide natural ventilation, reducing reliance on air conditioning.
The careful consideration of the flow between rooms is essential. Minimizing hallways and maximizing the use of transition spaces can contribute to a more efficient layout. The placement of bedrooms and bathrooms should be strategically planned to ensure privacy and minimize noise transfer. Utilizing pocket doors instead of traditional swing doors can also save space and improve accessibility.
The use of high ceilings can create a feeling of spaciousness, even in a small home. Vaulted or cathedral ceilings can draw the eye upward, making the room feel larger and more airy. Clerestory windows, placed high on the walls, can bring in additional natural light while maintaining privacy. These architectural details can significantly enhance the overall livability of a small home.
Design Styles and Aesthetic Considerations
Single story small homes can be adapted to various architectural styles, from traditional to contemporary. The choice of style should reflect the homeowner's personal preferences and the surrounding environment. A well-chosen design style can enhance the curb appeal of the home and create a cohesive aesthetic.
Craftsman style homes emphasize natural materials, such as wood and stone, and feature handcrafted details. Low-pitched roofs with wide eaves, exposed rafters, and gabled dormers are characteristic of this style. Craftsman homes often incorporate large porches, providing a welcoming outdoor space. The interior typically features built-in cabinetry, wainscoting, and other decorative elements.
Modern style homes are characterized by clean lines, minimalist design, and an emphasis on functionality. Flat roofs, large windows, and open floor plans are common features. Modern homes often incorporate sustainable materials and energy-efficient technologies. The interior is typically uncluttered and features simple, elegant furnishings.
Cottage style homes evoke a sense of charm and warmth. They often feature small, cozy rooms, low ceilings, and decorative details such as window boxes and flower gardens. Cottage homes typically have a relaxed and inviting atmosphere. The exterior is often adorned with colorful paint, decorative trim, and charming landscaping.
Ranch style homes are known for their single-level design, low-pitched roofs, and attached garages. They are typically rectangular or L-shaped and feature large windows and sliding glass doors. Ranch homes are often designed for informal living and outdoor entertaining. The interior typically features open floor plans and spacious living areas.
The use of color, texture, and lighting can significantly impact the overall aesthetic of a small home. Light, neutral colors can make a space feel larger and brighter. Accent colors can be used to add visual interest and personality. Textural elements, such as wood, stone, and fabric, can add depth and warmth to the interior. Strategic lighting can enhance the ambiance of the home and highlight architectural features.
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Sustainable design principles are crucial in single story small home plans. Incorporating energy-efficient technologies and materials can significantly reduce the home's environmental impact and lower utility costs. A well-designed home can minimize energy consumption, conserve water, and promote healthy indoor air quality.
Proper insulation is essential for maintaining a comfortable indoor temperature and reducing energy loss. High-performance insulation materials, such as spray foam or fiberglass batts, can effectively seal the building envelope and prevent heat transfer. Insulating the walls, roof, and foundation can significantly reduce heating and cooling costs.
Energy-efficient windows and doors can also contribute to energy savings. Double-pane or triple-pane windows with low-E coatings can reduce heat gain in the summer and heat loss in the winter. Weather stripping and caulking can seal gaps around windows and doors, preventing air leaks. Choosing ENERGY STAR-certified windows and doors can ensure optimal energy performance.
Solar panels can provide a renewable source of energy for the home. Photovoltaic (PV) panels can convert sunlight into electricity, which can be used to power appliances, lighting, and other electrical devices. Solar panels can significantly reduce reliance on fossil fuels and lower electricity bills. Government incentives and tax credits may be available to help offset the cost of installing solar panels.
Water conservation measures can also reduce the environmental impact of a small home. Low-flow toilets, showerheads, and faucets can significantly reduce water consumption. Rainwater harvesting systems can collect rainwater for irrigation or other non-potable uses. Drought-tolerant landscaping can minimize the need for irrigation. Choosing water-efficient appliances, such as washing machines and dishwashers, can also contribute to water conservation.
The use of sustainable building materials can minimize the environmental impact of construction. Reclaimed wood, recycled content materials, and sustainably harvested lumber are environmentally friendly alternatives to conventional building materials. Choosing low-VOC (volatile organic compound) paints, adhesives, and finishes can promote healthy indoor air quality. Selecting durable and long-lasting materials can reduce the need for repairs and replacements, minimizing waste over the long term.
Proper ventilation is essential for maintaining healthy indoor air quality. Mechanical ventilation systems, such as energy recovery ventilators (ERVs) or heat recovery ventilators (HRVs), can exchange stale indoor air with fresh outdoor air while recovering heat or energy. Ventilation systems can remove pollutants, moisture, and odors from the home, improving air quality and reducing the risk of mold growth.
Landscaping can also play a role in sustainability. Planting trees and shrubs can provide shade, reducing the need for air conditioning in the summer. Native plants require less water and maintenance than non-native plants. Permeable paving materials, such as gravel or pavers, can reduce stormwater runoff and improve water infiltration. A well-designed landscape can enhance the aesthetic appeal of the home while also contributing to environmental sustainability.

48 Ideas House Plans One Story Country Front Elevation For 2024 Remodelhouseplans Small Layout Floor Tiny

10 Small House Plans With Open Floor Blog Homeplans Com

Unique One Story House Plans Monster

Small One Story 2 Bedroom Retirement House Plans Houseplans Blog Com

Small One Story 2 Bedroom Retirement House Plans Houseplans Blog Com

Stylish One Story House Plans Blog Eplans Com

Best One Story House Plans And Ranch Style Designs

Small Cabin House Plans Floor Construction Guest
Must Have One Story Open Floor Plans Blog Eplans Com
10 Small House Plans With Open Floor Blog Homeplans Com