Single-Family Home Plan Designs: A Comprehensive Guide
Single-family home plan designs represent the blueprint for a dwelling intended for occupancy by a single family unit. These plans encapsulate a multitude of architectural, structural, and aesthetic considerations to create a habitable and functional living space. The selection of an appropriate home plan design is a crucial step in the home-building process, influencing not only the initial construction but also the long-term comfort, value, and livability of the residence.
The design process begins with a thorough assessment of the homeowner's needs, lifestyle, budget, and preferences. This initial stage involves determining the desired square footage, the number of bedrooms and bathrooms, the preferred layout, and any specific features or amenities. These requirements are then translated into a detailed set of drawings and specifications that guide the construction team.
The complexity of single-family home plan designs varies significantly, ranging from simple, cost-effective layouts to elaborate, custom-designed residences. Factors such as the geographical location, climate, site conditions, and local building codes also play a significant role in shaping the final design.
Essential Elements of Single-Family Home Plan Designs
A comprehensive single-family home plan design encompasses several key elements, each contributing to the overall functionality and structural integrity of the building. These elements are typically organized into different sets of drawings and specifications, providing a clear and detailed roadmap for the construction process.
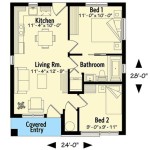
Floor Plans: These are perhaps the most fundamental component of any home plan design. Floor plans provide a two-dimensional representation of each level of the house, illustrating the layout of rooms, hallways, and other interior spaces. They specify the dimensions of each room, the location of doors and windows, and the placement of essential fixtures such as plumbing and electrical outlets. Floor plans are instrumental in visualizing the flow of movement within the house and ensuring that the space is utilized efficiently.
Elevation Drawings: Elevation drawings depict the exterior appearance of the house from different viewpoints, typically showing the front, rear, and side elevations. These drawings illustrate the architectural style of the house, including the roofline, window and door placement, and exterior finishes. Elevation drawings are crucial for visualizing the aesthetic appeal of the house and ensuring that it complements its surroundings.
Foundation Plans: Foundation plans detail the construction of the foundation, which serves as the base upon which the entire house rests. These plans specify the type of foundation (e.g., slab-on-grade, crawl space, or basement), the dimensions and materials of the foundation walls, and the location of support beams and columns. A properly designed foundation is essential for ensuring the structural stability of the house and preventing issues such as settling or cracking.
Roof Plans: Roof plans outline the design and construction of the roof, including the roof pitch, the type of roofing materials, and the location of gutters and downspouts. The roof plays a critical role in protecting the house from the elements, and a well-designed roof is essential for preventing leaks and water damage. Roof plans also consider factors such as snow load and wind resistance, ensuring that the roof can withstand the environmental conditions of the area.
Electrical Plans: Electrical plans detail the location of electrical wiring, outlets, switches, and light fixtures throughout the house. These plans also specify the size and type of electrical circuits and the location of the electrical panel. Electrical plans must adhere to local electrical codes to ensure the safety of the occupants and prevent electrical hazards.
Plumbing Plans: Plumbing plans illustrate the layout of water supply lines, drain lines, and sewer lines within the house. These plans specify the location of plumbing fixtures such as sinks, toilets, showers, and bathtubs, as well as the location of hot water heaters and other plumbing equipment. Plumbing plans must comply with local plumbing codes to ensure the proper functioning of the plumbing system and prevent issues such as leaks or blockages.
HVAC Plans: HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) plans detail the design and installation of the heating and cooling systems in the house. These plans specify the location of furnaces, air conditioners, ductwork, and vents. HVAC plans are crucial for ensuring comfortable indoor temperatures and air quality throughout the year. They also consider energy efficiency, aiming to minimize energy consumption and reduce utility costs.
Factors Influencing Single-Family Home Plan Design Choices
The selection of a single-family home plan design is influenced by a myriad of factors, encompassing both practical and aesthetic considerations. Understanding these factors is crucial for making informed decisions and creating a home that meets the homeowner's specific needs and preferences.
Budget: The budget is often the most significant constraint in the home-building process. The cost of construction can vary widely depending on the size, complexity, and materials of the house. It is important to establish a realistic budget early on and select a home plan design that aligns with the available financial resources. Simplification of the design, such as opting for a simpler roofline or fewer custom features, can help to reduce construction costs.
Lot Size and Shape: The size and shape of the building lot can significantly influence the design of the house. A narrow lot, for example, may necessitate a vertically oriented house with multiple stories, while a large lot may allow for a sprawling single-story ranch-style home. The topography of the lot, including slopes and drainage patterns, must also be considered to ensure proper site grading and prevent water damage.
Lifestyle and Needs: The lifestyle and needs of the occupants are paramount considerations in the home plan design process. A family with young children may prioritize a large, open-plan living area and a dedicated playroom, while a retired couple may prefer a smaller, low-maintenance home with a focus on accessibility. Specific needs, such as home offices, guest rooms, or storage space, should also be factored into the design.
Architectural Style: Architectural style refers to the aesthetic characteristics of the house, including its shape, form, and detailing. Common architectural styles include traditional styles such as Colonial, Victorian, and Craftsman, as well as modern styles such as contemporary, minimalist, and mid-century modern. The choice of architectural style is largely a matter of personal preference, but it is important to select a style that complements the surrounding neighborhood and adheres to any applicable architectural guidelines.
Energy Efficiency: Energy efficiency is an increasingly important consideration in home plan design. Incorporating energy-efficient features such as high-performance windows, insulation, and HVAC systems can significantly reduce energy consumption and lower utility costs. Passive solar design, which utilizes the sun's energy for heating and lighting, can also be incorporated into the design to further enhance energy efficiency. Building codes often mandate minimum energy efficiency standards, which must be adhered to during the design and construction process.
Universal Design Principles: Universal design principles aim to create homes that are accessible and usable by people of all ages and abilities. These principles include features such as wider doorways, ramps, grab bars, and accessible kitchen and bathroom layouts. Incorporating universal design principles into the home plan design can make the house more comfortable and convenient for all occupants, regardless of their physical limitations. This is particularly important for homeowners who plan to age in place.
Navigating the Single-Family Home Plan Design Process
The process of selecting and implementing a single-family home plan design can be complex and time-consuming. Engaging with qualified professionals, such as architects, designers, and builders, is essential for navigating this process successfully.
Consulting with an Architect: An architect is a licensed professional who specializes in the design of buildings. An architect can help homeowners to translate their needs and preferences into a detailed set of drawings and specifications that meet their budget and comply with all applicable building codes. Architects also provide valuable guidance throughout the construction process, ensuring that the design is implemented accurately and effectively.
Working with a Designer: A designer can assist with the interior layout and aesthetic elements of the house. Designers can help homeowners to select appropriate finishes, fixtures, and furnishings that complement the architectural style of the house and create a cohesive and visually appealing living space. Designers can also provide valuable advice on space planning and furniture placement to maximize functionality and comfort.
Selecting a Builder: The builder is responsible for constructing the house according to the approved plans and specifications. It is important to select a builder with a proven track record of quality workmanship and a strong understanding of building codes and best practices. Obtaining multiple bids from different builders and carefully reviewing their qualifications and references is essential for making an informed decision.
Obtaining Permits and Approvals: Before construction can begin, it is necessary to obtain all required permits and approvals from local government agencies. These permits typically include building permits, electrical permits, plumbing permits, and HVAC permits. The permitting process can be time-consuming, and it is important to factor this into the overall project timeline. The architect or builder can often assist with the permitting process, ensuring that all necessary documentation is submitted correctly and in a timely manner.
Managing the Construction Process: The construction process requires careful management to ensure that the project stays on schedule and within budget. Regular communication between the homeowner, architect, designer, and builder is essential for addressing any issues or concerns that may arise. Regular site visits are also important for monitoring the progress of the construction and ensuring that the work is being performed to the required standards.

Affordable Single Family Detached Home Designs Pro Builder

Single Family Home Design Cad Pro

Top 10 Duplex Plans That Look Like Single Family Homes Houseplans Blog Com

Single Family 2 Story Houses Home Plans Unique House Floor Pl Two Design

Affordable Single Family Detached Home Designs Pro Builder

Top 10 Duplex Plans That Look Like Single Family Homes Houseplans Blog Com
The Best Home Designs For Family Entertaining C Homes

Acacia Home Design Single Y Display Rawson Homes House Plans Bungalow Floor Narrow

House Plan Designs For Single Family Built To Homes

Our Best Tiny Country House Plans And Small Designs