Shed House Plans 2 Bedroom: A Comprehensive Guide
The concept of a "shed house," often referred to as a shouse, has gained significant traction as a viable and efficient housing alternative. A shed house generally involves converting a pre-engineered metal building, or designing a new one, into a residential dwelling. This often provides a cost-effective solution compared to traditional stick-built homes, allowing for customization and adaptability to specific lifestyle needs. Among the various configurations, the 2-bedroom shed house plan offers a balanced blend of affordability, space, and functionality, making it attractive to small families, couples, or individuals seeking a more streamlined living environment.
Designing a 2-bedroom shed house requires careful consideration of numerous factors, ranging from local building codes and zoning regulations to budget constraints and personal preferences. Selecting the appropriate shed house plan is equally crucial, as it dictates the overall layout, structural integrity, and aesthetic appeal of the dwelling. This article explores the essential considerations involved in planning a 2-bedroom shed house, focusing on key aspects such as design, costs, legal requirements, and maximizing space utilization.
Key Point 1: Design Considerations for 2-Bedroom Shed House Plans
The design phase is arguably the most critical aspect of constructing a 2-bedroom shed house. It encompasses various elements that collectively determine the functionality and comfort of the living space. These elements include the overall layout, room dimensions, material selection, and incorporation of essential utilities.
Layout and Floor Plan:
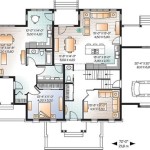
The layout of a 2-bedroom shed house should prioritize efficient space utilization. A well-designed floor plan minimizes wasted space and maximizes the usability of each room. Open-concept designs that combine the living area, dining area, and kitchen are popular choices for shed houses, as they create a more spacious and inviting atmosphere. Careful planning is required to delineate distinct functional zones within the open space while maintaining a cohesive aesthetic. The placement of bedrooms should consider privacy and noise insulation, often situated away from the main living areas.Room Dimensions:
The dimensions of each room should be carefully planned to accommodate furniture and occupants comfortably. Minimum room size requirements are often dictated by local building codes, which must be adhered to. Master bedrooms typically require more space than secondary bedrooms, often including features such as walk-in closets and en-suite bathrooms. The living area should be large enough to accommodate seating, entertainment systems, and potentially a home office setup. Kitchen dimensions should be adequate for food preparation, storage, and potentially a breakfast bar or island.Material Selection:
The choice of building materials significantly impacts the cost, durability, and aesthetic appeal of the shed house. Materials commonly used in shed house construction include metal siding, wood framing, concrete slabs, and various insulation options. Metal siding is a popular choice due to its durability, low maintenance requirements, and fire resistance. However, it may require additional insulation to improve energy efficiency and soundproofing. Wood framing provides a more traditional look and can be more easily modified, but it requires more maintenance to prevent rot and insect infestation. Concrete slabs provide a stable and durable foundation for the structure.Utility Integration:
Integrating essential utilities such as plumbing, electrical, and HVAC systems is a fundamental aspect of shed house design. Proper planning is crucial to ensure that these systems are installed safely and efficiently. Plumbing systems must be designed to provide adequate water pressure and drainage for bathrooms, kitchens, and laundry areas. Electrical systems must be sized to accommodate the electrical load of appliances, lighting, and other electrical devices. HVAC systems must be chosen to provide adequate heating and cooling while maintaining energy efficiency. Integrating renewable energy sources, such as solar panels, can further reduce utility costs and environmental impact.Key Point 2: Cost Considerations and Budgeting
The cost of building a 2-bedroom shed house can vary significantly depending on several factors, including the size of the structure, the quality of materials used, the complexity of the design, and the location of the construction site. Developing a detailed budget is essential to ensure that the project stays within financial constraints.
Material Costs:
Material costs typically account for a significant portion of the overall budget. Prices for lumber, metal siding, roofing materials, insulation, windows, doors, and plumbing fixtures can fluctuate depending on market conditions and supplier agreements. Obtaining multiple quotes from different suppliers is recommended to secure the best possible prices. Consider exploring alternative materials that offer similar performance characteristics at a lower cost.Labor Costs:
Labor costs can also vary significantly depending on the region and the skill level of the contractors hired. Hiring experienced and qualified contractors is essential to ensure that the work is performed to a high standard. Obtaining multiple bids from different contractors is recommended to compare prices and assess their qualifications. Consider performing some of the work yourself, such as painting or landscaping, to reduce labor costs. However, avoid attempting tasks that require specialized skills or knowledge, as this could result in costly mistakes.Permitting and Fees:
Obtaining the necessary building permits and paying associated fees is a mandatory aspect of shed house construction. Permit requirements and fees vary depending on local regulations. Researching local zoning regulations and building codes is essential to ensure that the project complies with all applicable requirements. Failure to obtain the necessary permits can result in fines and delays. Budgeting for permit fees and inspections is crucial to avoid unexpected expenses.Unexpected Costs:
It is prudent to allocate a contingency fund to cover unexpected costs that may arise during construction. Unexpected costs can include unforeseen site conditions, material price increases, or changes to the design. A contingency fund of 10-15% of the total project budget is generally recommended. Having a contingency fund can provide peace of mind and prevent the project from derailing due to unforeseen circumstances.Key Point 3: Legal and Regulatory Requirements
Constructing a shed house involves navigating a complex web of legal and regulatory requirements. These requirements are designed to ensure the safety and well-being of occupants and the surrounding community. Compliance with these requirements is mandatory and can significantly impact the design, cost, and timeline of the project.
Zoning Regulations:
Zoning regulations dictate how land can be used within a particular jurisdiction. These regulations typically specify minimum lot sizes, setback requirements, height restrictions, and other limitations. Before embarking on shed house construction, it is essential to research local zoning regulations to ensure that the project complies with all applicable requirements. Zoning regulations may also restrict the types of structures that can be built on a particular property.Building Codes:
Building codes establish minimum standards for the design and construction of buildings. These codes are designed to ensure the structural integrity, fire safety, and energy efficiency of buildings. Building codes vary depending on the jurisdiction and may be based on national model codes such as the International Building Code (IBC) or the International Residential Code (IRC). Compliance with building codes is mandatory and requires obtaining building permits and undergoing inspections.Permitting Process:
The permitting process involves submitting construction plans to the local building department for review and approval. The building department will review the plans to ensure that they comply with all applicable zoning regulations and building codes. Once the plans are approved, a building permit will be issued, allowing construction to commence. Inspections are typically required at various stages of construction to ensure that the work is being performed in accordance with the approved plans and building codes.Easements and Restrictive Covenants:
Easements and restrictive covenants are legal agreements that may restrict the use of a property. Easements grant specific rights to third parties, such as utility companies, to access or use a portion of the property. Restrictive covenants are private agreements that restrict the use of the property in certain ways, such as prohibiting certain types of structures or activities. Before constructing a shed house, it is essential to review the property's title report to identify any easements or restrictive covenants that may affect the project.Careful planning, meticulous budgeting, and diligent adherence to legal and regulatory requirements are essential for the successful construction of a 2-bedroom shed house. By considering these factors, individuals can create a cost-effective, functional, and comfortable living space that meets their specific needs and preferences.

16 X 40 Floor Plans For 2 Br

Pin Page

Shed Roof Cabin House 2 Bedroom 20 X 44 Ibra Plans

Tiny Home Floor Plan Gallery Robin Sheds

Tiny Home Floor Plan Gallery Robin Sheds

Affordable Shed House Construction Ideas

House Plans 10x8 With 2 Bedrooms Shed Roof 3d 20c

House Front Shed Design 36x22 2 Beds 1 Bath Samhouseplans

House Design Plans 6 5x8 With 2 Bedrooms Shed Roof S 909

Small House Plans 6 7 With 2 Bedrooms Shed Roof Engineering Discoveries