Plans For Tiny Homes On Wheels: A Comprehensive Guide
The allure of minimalist living, combined with the freedom of mobility, has fueled the burgeoning popularity of tiny homes on wheels (THOWs). These dwellings, typically built on trailer frames, offer a viable alternative to traditional housing, appealing to individuals seeking affordability, environmental consciousness, and a nomadic lifestyle. However, embarking on a THOW project requires careful planning and access to reliable plans. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the key considerations involved in obtaining and utilizing plans for tiny homes on wheels.
Before delving into the specifics of plans, it's crucial to understand the legal and regulatory landscape surrounding THOWs. Building codes, zoning ordinances, and DMV regulations vary significantly by jurisdiction. Some areas classify THOWs as recreational vehicles (RVs), while others treat them as accessory dwelling units (ADUs). A thorough investigation of local requirements is paramount to ensure compliance and avoid potential legal issues. This research should be conducted before investing in plans or commencing construction.
Furthermore, the design and construction of a THOW require a solid understanding of structural engineering, electrical systems, plumbing, and weight distribution. A poorly designed or constructed THOW can pose significant safety risks, especially during transit. Consequently, relying on professional plans or seeking guidance from experienced builders is highly recommended.
Understanding the Different Types of THOW Plans
Tiny home on wheels plans come in various formats, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. It's important to carefully evaluate these options to determine the best fit for individual skill levels, budget constraints, and desired level of customization.
Stock Plans: These are pre-designed blueprints offered by numerous companies specializing in tiny home design. Stock plans typically encompass a wide range of styles and sizes, providing a relatively affordable and readily available option. They often include detailed floor plans, elevations, sections, and material lists. The primary advantage of stock plans is their cost-effectiveness and convenience. However, they may lack the flexibility to accommodate specific individual needs or aesthetic preferences.
Custom Plans: For those seeking a truly unique and personalized THOW, custom plans are the preferred choice. This involves working directly with an architect or designer to create a tailored design that reflects individual needs, preferences, and site constraints. Custom plans offer the highest degree of flexibility and control over the final product. However, they are generally more expensive and time-consuming than stock plans. The process involves detailed consultations, iterative design revisions, and potentially engineering certifications.
DIY Plans and Resources: A plethora of online resources offer free or low-cost DIY plans for tiny homes on wheels. These resources can be a valuable starting point for individuals with prior construction experience or a strong desire to learn. However, it's crucial to exercise caution when using DIY plans, as their quality and accuracy can vary significantly. Always verify the structural integrity of the design and ensure compliance with local building codes. It's also advisable to supplement DIY plans with professional guidance or consult with experienced builders on specific aspects of the project.
The choice between stock, custom, and DIY plans hinges on factors such as budget, skill level, desired level of customization, and the complexity of the design. Individuals with limited construction experience or those seeking a specific design aesthetic may benefit from engaging a professional designer or builder.
Essential Elements to Consider When Evaluating THOW Plans
Selecting the right plans for a tiny home on wheels requires careful consideration of several key elements. These elements contribute to the structural integrity, functionality, and overall livability of the THOW.
Structural Integrity: The plans must clearly specify the structural components, including framing materials, wall thicknesses, roof design, and foundation details. The structural design should be engineered to withstand the stresses of transportation, including wind loads, vibrations, and potential impacts. It's essential to ensure that the plans comply with relevant building codes and engineering standards.
Weight Distribution: Proper weight distribution is crucial for safe towing and handling. The plans should indicate the location of heavy appliances, water tanks, and other components to ensure that the weight is evenly distributed across the trailer axle(s). An unbalanced THOW can be difficult to control and may pose a safety hazard on the road. Furthermore, the total weight of the THOW must remain within the trailer's weight capacity.
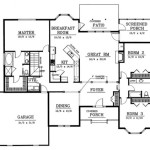
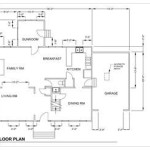
Floor Plan and Functionality: The floor plan should maximize the usable space and provide a comfortable and functional living environment. Consider factors such as the location of the kitchen, bathroom, sleeping area, and living space. Optimize storage solutions to minimize clutter and maximize space efficiency. Ensure adequate natural light and ventilation. The design should accommodate the individual's lifestyle and needs.
Electrical and Plumbing Systems: The plans should include detailed schematics for the electrical and plumbing systems. These schematics should specify the location of wiring, outlets, fixtures, and appliances. The electrical system should be designed to meet the anticipated power demands and comply with electrical codes. The plumbing system should include provisions for water supply, drainage, and waste disposal. Consider sustainable options such as solar panels, rainwater harvesting, and composting toilets.
Materials and Construction Techniques: The plans should specify the types of materials to be used in the construction of the THOW. Consider factors such as durability, weight, cost, and environmental impact. Choose materials that are lightweight, strong, and resistant to moisture and pests. Select construction techniques that are appropriate for the chosen materials and the overall design.
Compliance with Regulations: The plans must comply with all applicable building codes, zoning ordinances, and DMV regulations. Verify that the design meets the requirements for size, height, width, and weight. Obtain the necessary permits and inspections before commencing construction. Failure to comply with regulations can result in fines, delays, and potentially the inability to legally use the THOW.
Key Considerations for Adapting and Modifying THOW Plans
Even with well-designed plans, some degree of adaptation or modification may be necessary to suit individual needs or site-specific conditions. However, it's crucial to approach these modifications with caution and seek professional guidance when necessary.
Structural Modifications: Any modifications to the structural components of the THOW should be reviewed and approved by a qualified structural engineer. Changes to the framing, roof, or foundation can significantly impact the structural integrity of the dwelling. Unauthorized modifications may compromise the safety and stability of the THOW.
Electrical and Plumbing Modifications: Changes to the electrical or plumbing systems should be performed by licensed professionals. Incorrect wiring or plumbing can pose serious safety risks, including electrical shock, fire, and water damage. Ensure that all modifications comply with relevant electrical and plumbing codes.
Weight Distribution Adjustments: Modifications that affect the weight distribution of the THOW should be carefully evaluated to ensure they do not exceed the trailer's weight capacity or compromise stability. Consider the impact of adding or removing heavy appliances, water tanks, or other components. Consult with a trailer specialist or engineer to assess the suitability of any proposed weight distribution adjustments.
Accessibility Considerations: If accessibility is a concern, the plans may need to be modified to accommodate individuals with disabilities. This may involve widening doorways, installing ramps, and providing accessible bathroom fixtures. Consult with an accessibility specialist to ensure that the modifications comply with accessibility standards.
Material Substitutions: While material substitutions may be necessary due to availability or cost considerations, it's important to ensure that the substitute materials are comparable in terms of strength, durability, and weight. Consult with a building materials supplier or engineer to determine the suitability of alternative materials.
Permitting Implications: Any significant modifications to the plans may require additional permits or inspections. Check with the local building department to determine the permitting requirements for the proposed modifications. Failure to obtain the necessary permits can result in fines and delays.
In conclusion, obtaining and utilizing plans for tiny homes on wheels requires careful consideration of legal requirements, design principles, and construction techniques. By thoroughly researching available options, evaluating essential elements, and approaching modifications with caution, individuals can ensure the successful construction of a safe, functional, and aesthetically pleasing THOW.

Tiny House Floor Plans 32 Home On Wheels Design

Escape Traveler A Tiny House On Wheels That Comfortably Sleeps 6 Floor Plans Trailer

Tiny House Floor Plans 32 Long Home On Wheels Design

Design A Tiny House On Wheels Tips And Tools For Diyers

224 Sq Ft Tiny House On Wheels By Living Homes Small Diy Floor Plans

Tiny House Plans The Project

Free Tumbleweed Diy Tiny House Plans Houses

How To Pick The Best Tiny House On Wheels Floor Plan Wayward Home

27 Adorable Free Tiny House Floor Plans Craft Mart

Floor Plans For Your Tiny House On Wheels Photos