2 Story Colonial Home Plans: A Comprehensive Overview
The 2-story Colonial home plan remains a popular choice for homeowners seeking a blend of historical charm and modern functionality. Characterized by their symmetrical facades, centered entryways, and efficient use of space, these homes offer a timeless appeal that transcends architectural trends. This article will delve into the key aspects of 2-story Colonial home plans, examining their historical roots, common features, design variations, and considerations for modern living.
Colonial architecture in the United States evolved from various European styles brought by early settlers. From the original British Colonial designs of the Eastern seaboard, which often featured simple, boxy structures, the style matured and diversified into distinct regional variations. These included the Georgian Colonial, known for its more elaborate detailing and symmetrical proportions, and the Dutch Colonial, easily identified by its distinctive gambrel roof. Regardless of the specific iteration, the underlying principles of efficiency, practicality, and balanced aesthetics remained consistent.
This architectural style offered practical solutions to the constraints faced by early settlers. The two-story design maximized living space on relatively compact plots of land. The symmetrical layout and central hallway facilitated efficient traffic flow throughout the house. The use of durable materials like wood and brick ensured longevity and resilience in harsh climates. These initial advantages continue to resonate with homeowners today, contributing to the enduring popularity of Colonial home plans.
Key Features of 2-Story Colonial Home Plans
Several defining features consistently appear in 2-story Colonial home plans, distinguishing them from other architectural styles. These features contribute to both the aesthetic appeal and the functional layout of the home.
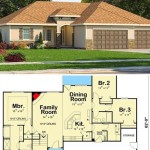
Symmetrical Façade: The hallmark of a Colonial home is its symmetrical front elevation. The entryway is typically centered, with an equal number of windows on either side. This symmetry extends to the roofline, which is usually a simple gable roof. This emphasis on balance creates a sense of order and visual harmony.
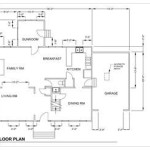
Central Entryway and Hallway: A prominent front door leads into a central hallway that runs directly through the middle of the house. This hallway serves as the main artery, providing access to the various rooms on the first floor, such as the living room, dining room, and kitchen. A staircase, often located near the entryway, leads to the bedrooms on the second floor.
Rectangular Floor Plan: Colonial homes typically feature a rectangular or square floor plan. This simple shape maximizes the living space and simplifies construction. While variations exist, the foundational rectangular form is a common characteristic. This shape is inherently efficient in terms of construction and resource utilization.
Formal Living Spaces: Traditionally, Colonial homes included formal living spaces designed for entertaining guests. These rooms, such as the living room and dining room, were often located at the front of the house and were more elaborately decorated than the more casual family spaces.
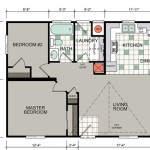
Second-Floor Bedrooms: The second floor of a Colonial home is typically dedicated to bedrooms. This arrangement provides privacy and separation between the living areas and the sleeping quarters. The number of bedrooms can vary depending on the size of the house and the needs of the occupants.
Gable Roof: A gable roof, characterized by two sloping sides that meet at a ridge, is the most common roof type for Colonial homes. This simple and efficient roof design provides adequate drainage and is relatively easy to construct. Dormers may be added to the roof to provide additional light and ventilation to the second floor.
Design Variations and Sub-Styles of Colonial Homes
While sharing core characteristics, Colonial architecture has evolved into several distinct sub-styles, each reflecting regional influences and historical trends. Understanding these variations allows for a more nuanced appreciation of Colonial home plans.
Georgian Colonial: This style, popular during the 18th century, is characterized by its refined details and symmetrical proportions. Georgian Colonials often feature ornate doorways with decorative pilasters and pediments, as well as multi-pane windows and dentil molding along the eaves. The use of brick is common, providing a sense of substance and permanence.
Federal Colonial: Emerging after the American Revolution, the Federal Colonial style incorporated elements of Georgian architecture but with a more distinctly American flair. Federal Colonials often feature elliptical fanlights above the front door, delicate ornamentation, and lighter, more airy interiors. The use of painted wood siding became more prevalent.
Dutch Colonial: The defining feature of the Dutch Colonial style is its gambrel roof, which slopes gently downwards before sharply flaring outwards. This roof design provides more headroom on the second floor and creates a distinctive silhouette. Dutch Colonials often feature dormers and wide front porches.
Cape Cod Colonial: Originating in New England, the Cape Cod Colonial is a simpler, more compact version of the Colonial style. These homes typically feature a central chimney, a low-pitched gable roof, and minimal ornamentation. Their inherent simplicity and practicality made them well-suited to the harsh New England climate.
Spanish Colonial: Predominantly found in the Southwestern United States, the Spanish Colonial style incorporates elements of Spanish architecture, such as stucco walls, red tile roofs, and arched doorways. These homes often feature courtyards and patios, reflecting the outdoor lifestyle of the region.
Considerations for Modern Living in 2-Story Colonial Homes
While Colonial home plans offer timeless appeal, adapting them to modern living requires careful consideration of contemporary needs and preferences. Integrating modern amenities and design elements while preserving the historical integrity of the home is a key challenge for homeowners.
Open Floor Plans: Traditional Colonial homes often feature separate, enclosed rooms. Many modern homeowners prefer open floor plans that create a more spacious and interconnected living environment. Combining the kitchen, dining area, and living room into a single open space can enhance functionality and facilitate social interaction.
Updated Kitchens and Bathrooms: Modern kitchens and bathrooms require updated appliances, fixtures, and finishes. Integrating these modern elements into a Colonial-style home requires careful planning to ensure that the overall aesthetic remains consistent. Selecting classic materials and finishes that complement the historical character of the home is crucial.
Energy Efficiency: Older Colonial homes may lack adequate insulation and energy-efficient windows. Upgrading these elements is essential for reducing energy consumption and improving comfort. Installing energy-efficient windows, adding insulation to the walls and attic, and upgrading the heating and cooling systems can significantly reduce utility bills.
Accessibility: Traditional Colonial homes may not be easily accessible for individuals with mobility limitations. Adding ramps, installing elevators, or modifying doorways can improve accessibility and make the home more inclusive.
Outdoor Living Spaces: Modern homeowners increasingly value outdoor living spaces. Adding a porch, patio, or deck can extend the living area and provide opportunities for relaxation and entertainment. These outdoor spaces can be designed to complement the Colonial style of the home, using materials and finishes that are consistent with the overall aesthetic.
Technological Integration: Integrating modern technology, such as smart home systems, requires careful planning to avoid disrupting the historical character of the home. Concealing wiring and selecting discreetly designed devices can help to minimize the visual impact of these technologies.
Maintaining Historical Accuracy: When renovating or remodeling a Colonial home, it is important to maintain the historical accuracy of the design. Researching the original architectural details and using historically appropriate materials and finishes can help to preserve the integrity of the home.
2-story Colonial home plans offer a compelling combination of historical charm and functional living space. By understanding the key features, design variations, and considerations for modern living, homeowners can create a home that is both beautiful and practical and meets their evolving needs.

2 Story Colonial Duncan House Plans Craftsman Traditional

Colonial Style House Plan 4 Beds 2 5 Baths 1895 Sq Ft 23 2479 Dreamhomesource Com

1924 Southern Pine Assn Plan 3029 Colonial House Plans Sims Model

3 Bedroom 2 Story Southern Colonial House Plan With Study And Wrap Around Porch Charleston Plans Farmhouse Family

Colonial Style House Plans For A 2 Story 4 Bedroom Home

Brick Home Plan With Seven Bedrooms 4711 Grand Colonial 2902

Colonial House Plans The Plan

Colonial Style House Plan 2 Beds Baths 1169 Sq Ft 17 1120 Country Design Traditional Plans Garage

2 Story 5 Bedroom Colonial Home With Library House Plan

Colonial Home Plans House