Home Plans Under 1000 Sq Ft: A Comprehensive Guide
The appeal of small home plans, particularly those under 1000 square feet, has grown significantly in recent years. This surge in popularity stems from a confluence of factors, including affordability, downsizing trends, environmental consciousness, and the desire for simpler living. These compact homes are not merely scaled-down versions of larger houses; instead, they necessitate careful planning and innovative design to maximize functionality and comfort within a reduced footprint. This article will explore the intricacies of home plans under 1000 square feet, examining key considerations, design strategies, and popular styles.
The allure of a smaller home extends beyond mere cost savings. Many individuals and families are drawn to the reduced maintenance requirements, lower utility bills, and the overall decrease in clutter that accompanies a smaller living space. Furthermore, the growing awareness of environmental impact encourages individuals to consider smaller homes, minimizing their carbon footprint through reduced energy consumption and material usage. For others, small homes represent a conscious choice to prioritize experiences and financial freedom over material possessions, aligning with a minimalist lifestyle.
However, designing and building a home under 1000 square feet presents unique challenges. Every square inch must be carefully considered and strategically utilized. Space planning becomes paramount, and designers must employ creative solutions to address storage needs, maximize natural light, and ensure comfortable living spaces. The success of a small home hinges on thoughtful design that optimizes functionality and minimizes wasted space.
Key Considerations Before Selecting a Home Plan
Prior to embarking on the selection process for a home plan under 1000 square feet, several key considerations must be addressed. These considerations will significantly influence the choice of plan and the overall design approach.
Needs Assessment: A thorough needs assessment is the first and most crucial step. This involves a detailed evaluation of the homeowner's lifestyle, daily routines, and long-term goals. Key questions to consider include: How many occupants will reside in the home? What are the essential activities that will take place within the space (e.g., cooking, working from home, entertaining)? What are the storage requirements for personal belongings, hobby equipment, or seasonal items? Understanding these needs will inform the floor plan layout, the type of rooms required, and the necessary storage solutions.
Budget: Establishing a realistic budget is paramount. Building costs can vary significantly depending on the location, the complexity of the design, and the quality of materials used. It is essential to obtain detailed estimates from contractors and account for all expenses, including land acquisition (if applicable), permits, construction labor and materials, landscaping, and interior finishes. A well-defined budget will guide the selection of a home plan that is both aesthetically pleasing and financially feasible.
Zoning and Building Codes: Local zoning regulations and building codes impose specific requirements on the size, location, and construction of homes. These regulations may dictate minimum lot sizes, setback requirements, height restrictions, and energy efficiency standards. It is imperative to consult with local authorities and obtain the necessary permits before commencing any construction activity. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in costly delays and legal repercussions.
Site Analysis: The characteristics of the building site will significantly influence the design and orientation of the home. Factors such as topography, soil conditions, solar orientation, and prevailing winds should be carefully analyzed. A sloped lot, for example, may require a different foundation design than a flat lot. Optimizing solar orientation can maximize natural light and reduce energy consumption for heating and cooling. Understanding these site-specific factors will ensure that the home is well-suited to its environment and performs optimally.
Design Strategies for Maximizing Space
Designing a home under 1000 square feet requires employing specific strategies to maximize every inch of available space. These strategies focus on multi-functional spaces, efficient layouts, and clever storage solutions.
Open Floor Plans: Open floor plans are a common and effective strategy for creating a sense of spaciousness in small homes. By eliminating walls between living areas, such as the kitchen, dining room, and living room, the interior feels more expansive and airy. This design approach also promotes better natural light penetration and encourages social interaction.
Multi-Functional Spaces: To optimize limited square footage, consider designing spaces that can serve multiple purposes. For example, a guest bedroom could double as a home office or a hobby room. A dining table could also function as a workspace. Furniture that can be easily converted or reconfigured is particularly valuable in multi-functional spaces.
Vertical Space Utilization: Capitalizing on vertical space is crucial in small homes. High ceilings can create a sense of grandeur and allow for the incorporation of storage solutions that extend upwards. Loft spaces can be used for sleeping areas, home offices, or storage. Vertical shelving and cabinets can provide ample storage without encroaching on valuable floor space.
Built-In Storage: Built-in storage solutions are highly effective in small homes. These custom-designed units can be integrated seamlessly into the architecture, maximizing storage capacity while minimizing clutter. Examples include built-in bookshelves, window seats with storage compartments, and under-bed storage drawers.
Strategic Use of Mirrors: Mirrors can create the illusion of increased space and reflect natural light, making a small room feel larger and brighter. Strategically placed mirrors on walls or doors can significantly enhance the sense of spaciousness.
Natural Light and Ventilation: Maximizing natural light and ventilation is essential for creating a comfortable and inviting living environment in a small home. Large windows and skylights can bring in ample natural light, reducing the need for artificial lighting. Proper ventilation can prevent stale air and moisture buildup, contributing to a healthier indoor environment.
Popular Styles for Small Home Plans
Several architectural styles lend themselves well to small home designs, each offering unique aesthetic characteristics and functional advantages.
Cottage Style: Cottage-style homes are characterized by their charming and cozy aesthetics. They often feature steeply pitched roofs, dormer windows, and inviting porches. Cottage-style interiors typically incorporate natural materials, such as wood and stone, creating a warm and inviting atmosphere. The compact layout of cottage-style homes makes them well-suited for small home plans.
Modern Farmhouse: The modern farmhouse style blends traditional farmhouse elements with contemporary design features. These homes typically feature clean lines, neutral color palettes, and natural wood accents. Modern farmhouse interiors often incorporate open floor plans and ample natural light. This style is a popular choice for those seeking a blend of rustic charm and modern functionality in a small home.
Contemporary/Modern: Contemporary or modern home plans emphasize clean lines, minimalist aesthetics, and functional design. These homes often feature large windows, flat roofs, and open floor plans. Contemporary interiors typically incorporate sleek finishes, minimalist furniture, and a focus on natural light. The efficient and uncluttered design of contemporary homes makes them ideal for small spaces.
Bungalow: Bungalows are typically one-story or one-and-a-half-story homes with low-pitched roofs, wide eaves, and prominent front porches. Bungalows often feature open floor plans and built-in storage solutions. Their compact layout and emphasis on indoor-outdoor living make them well-suited for small home designs.
Tiny Homes: Tiny homes represent an extreme form of small home living, typically ranging from 100 to 400 square feet. These homes often incorporate innovative design features and sustainable materials. Tiny homes can be built on foundations or on trailers, offering flexibility in terms of location and mobility. While not suitable for everyone, tiny homes offer a unique and minimalist approach to small home living.
The selection of a home plan under 1000 square feet is a significant decision that requires careful consideration of various factors. By understanding the key considerations, employing effective design strategies, and exploring different architectural styles, individuals can create a functional, comfortable, and aesthetically pleasing small home that perfectly suits their needs and lifestyle.

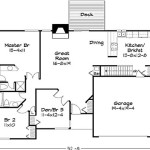
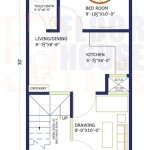
7 Ideal Small House Floor Plans Under 1 000 Square Feet Cottage

Our Top 1 000 Sq Ft House Plans Houseplans Blog Com

10 Modern Under 1000 Square Feet House Plans Craft Mart

10 Modern Under 1000 Square Feet House Plans Craft Mart

Small Cottage Plans Under 1000 Sq Ft Google Search House Floor

Our Top 1 000 Sq Ft House Plans Houseplans Blog Com

House Plans Under 1000 Square Feet
House Plan Of The Week 2 Beds Baths Under 1 000 Square Feet Builder
Small Country Ranch Plan 2 Bedrm Bath 1000 Sq Ft 141 1230

1000 Sq Ft Ranch House Plan 2 Bedrooms 1 Bath Porch